Welding is a process that involves joining metals together using high heat. It is a widely used technique in many industries, including construction, manufacturing, and automotive. One common challenge welders face is joining stainless steel to mild steel. In this article, we will discuss the process of welding stainless to mild steel using the MIG (Metal Inert Gas) method.
The MIG welding process, also known as Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), is a popular method for its ease of use and efficiency. It involves using a continuous solid wire electrode, shielded by a protective gas, which passes through a welding gun. MIG welding is widely used because it offers excellent control, high deposition rates, and produces clean welds.
When it comes to welding stainless to mild steel, there are a few factors to consider. The main challenge lies in the difference in composition between the two metals. Stainless steel contains a higher percentage of chromium and other alloying elements, which gives it superior corrosion resistance and strength. Mild steel, on the other hand, is a carbon steel with a smaller amount of alloying elements.

To weld stainless to mild steel successfully, it is necessary to maintain a balance between the two metals’ characteristics. This can be achieved by using a filler material that is compatible with both stainless and mild steel. One common choice for this purpose is a stainless steel filler wire.
When buying welding equipment for this specific application, it is important to ensure that you have the right tools and materials. A MIG welder capable of handling both stainless steel and mild steel is essential. Look for a welder with adjustable voltage and wire feed speed settings, as these will allow you to fine-tune the welding parameters according to the specific materials you are working with.
In terms of the protective gas, a mixture of argon and carbon dioxide (CO2) is commonly used for welding stainless to mild steel. This shielding gas provides excellent arc stability and reduces the risk of oxidation. Additionally, it helps to prevent contamination of the weld bead and ensures a clean and strong joint.
When it comes to the price of welding stainless to mild steel with MIG, it is important to consider the cost of the equipment, consumables, and labor. MIG welders can range in price depending on their capabilities and brand. It is important to invest in a high-quality welder that can handle the specific tasks required for welding stainless to mild steel.
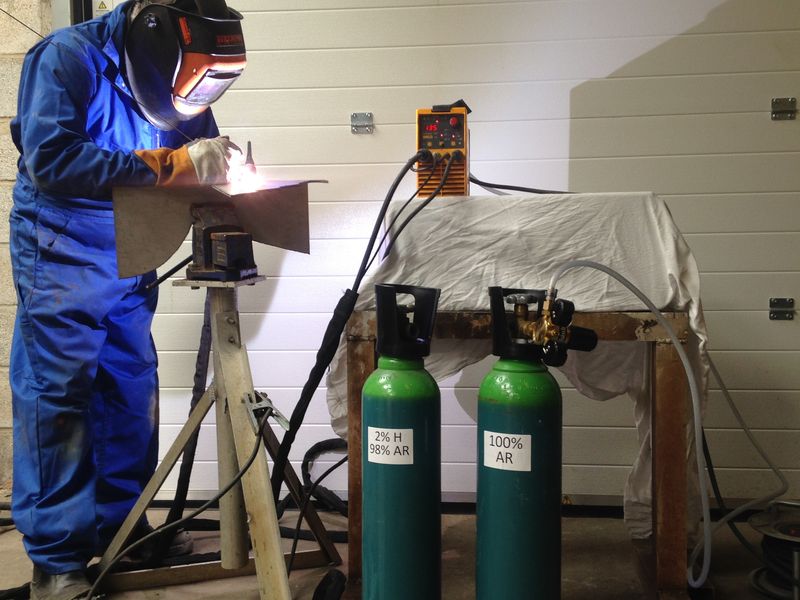

Additionally, the cost of the welding wire, shielding gas, and other consumables should be factored in. Stainless steel filler wire can be more expensive than mild steel wire, but it is necessary to ensure a strong and durable weld. The cost of the shielding gas will depend on the specific mixture used and the volume of gas consumed during the welding process.
Labor costs should also be considered, as welding stainless to mild steel requires skill and expertise. Hiring a professional welder who is experienced in this specific application may result in higher labor costs.
In conclusion, welding stainless to mild steel with MIG is a common and challenging task. By using the right tools and materials, such as a MIG welder with adjustable settings and a suitable stainless steel filler wire, it is possible to achieve strong and durable welds. The cost of the welding equipment, consumables, and labor are factors that should be taken into account when considering the overall price of the process.Additionally, it is important to consider the welding technique and process parameters when welding stainless to mild steel with MIG. Proper preparation of the joint is crucial for a successful weld. The surfaces of the metals should be clean and free from any contaminants, such as dirt, oil, and rust. It is recommended to use a wire brush or a grinder to remove any oxide layers or scale before welding.
Another aspect to consider is the choice of welding technique. There are different methods, such as butt joint or lap joint, that can be used depending on the application and desired strength of the weld. It is important to select the appropriate joint design to ensure optimal fusion and strength.

When setting the MIG welding parameters, the heat input and wire feed speed should be carefully chosen. The heat input affects the penetration and fusion of the metals, while the wire feed speed determines the amount of filler metal being added. It is recommended to start with lower settings and adjust as needed to achieve a proper weld bead appearance and weld strength. It is important to avoid excessive heat, as it can lead to distortion, warping, and degradation of the materials.
During the welding process, it is important to maintain proper shielding gas coverage. The shielding gas not only protects the weld from oxidation but also helps to stabilize the arc and improve the overall quality of the weld. Inadequate shielding can result in porosity, weld discontinuities, or inadequate fusion. Therefore, it is important to ensure that the gas flow rate is set correctly and that the gas nozzle is positioned close enough to the weld area to provide sufficient coverage.
Post-weld treatments may also be necessary when welding stainless to mild steel. Stainless steel has a tendency to form a heat-affected zone (HAZ) with reduced corrosion resistance due to the formation of chromium carbides. This can be mitigated by using post-weld treatments, such as passivation or pickling, to restore the stainless steel’s corrosion resistance.
In conclusion, welding stainless to mild steel with MIG can be a challenging task. However, with the right equipment, materials, and welding parameters, it is possible to achieve strong and durable welds. Proper joint preparation, selection of the appropriate welding technique, and careful adjustment of the MIG welding parameters are all critical for success. It is important to take into account the overall cost, including the price of the equipment, consumables, and labor, when considering welding stainless to mild steel with MIG. By following these guidelines, welders can ensure high-quality welds that meet the specific requirements of the application.