A Comprehensive Guide for Buyers
Introduction:
When it comes to welding, choosing the right electrode is crucial for achieving high-quality and long-lasting welds. Welding electrodes are classified based on various factors, including their coating composition, welding position, and intended application. In this article, we will delve into the classification of welding electrodes, explore essential factors to consider when buying them, and discuss their pricing dynamics.
Classification of Welding Electrodes:
1. Coating Composition:
Welding electrodes are commonly distinguished by the type of coating on their outer shell, as it significantly influences their performance and suitability for specific welding tasks. The primary coating compositions include:
a. Rutile Electrodes: These electrodes have a coating containing titanium dioxide (rutile) and are known for their smooth and stable arc performance. Rutile electrodes are commonly used for welding mild steel and are suitable for both AC and DC welding applications.

b. Cellulosic Electrodes: Ideal for vertical-down welding, cellulosic electrodes have a coating with a high cellulose content. They produce deep penetration and fast cooling welds, making them suitable for pipe welding and other applications requiring high-quality root welds.
c. Basic Electrodes: Basic electrodes have a coating composed of minerals such as calcium carbonate and calcium fluoride. These electrodes offer excellent mechanical properties, low hydrogen levels, and high resistance to cracking. They are widely used for welding steels and alloys, including stainless steels.
2. Welding Position:
Electrodes are also classified based on their suitability for specific welding positions or orientations. The most common classifications include:
a. Flat Electrodes (1): These electrodes are primarily designed for flat or horizontal welding positions, where gravity does not affect the weld pool significantly. They deliver stable, smooth arcs and are suitable for fabricating structures and plates.
b. Horizontal Electrodes (2): Designed for welding in the horizontal position, these electrodes provide good sidewall fusion and are commonly used for filling or cap passes in shipbuilding and structural steel welding.
c. Vertical Electrodes (3): Vertical electrodes are specifically designed for vertical welding positions. Their unique composition and coating enable them to maintain a stable arc, produce deep penetration, and prevent slag from rolling ahead of the weld pool.

3. Application-Specific Electrodes:
Apart from coating composition and welding position, welding electrodes are classified based on their intended application. Some common application-specific electrodes include:
a. Stainless Steel Electrodes: These electrodes are specifically designed for welding stainless steel, providing excellent corrosion resistance and weld quality. They often have a special coating that prevents the formation of chromium carbides, reducing the risk of intergranular corrosion.
b. Cast Iron Electrodes: Cast iron electrodes are specifically formulated to weld cast iron, which is known for its brittleness and low ductility. These electrodes have a special composition that allows for appropriate heating and cooling rates, minimizing the risk of cracking.
Buying Classification of Welding Electrodes:
When purchasing welding electrodes, several factors need to be considered to ensure the right choice for the intended welding task. These factors include:
1. Material Compatibility: Consider the base metal you will be welding and choose an electrode that is compatible with it. Different types of metals require different welding techniques and electrode compositions.
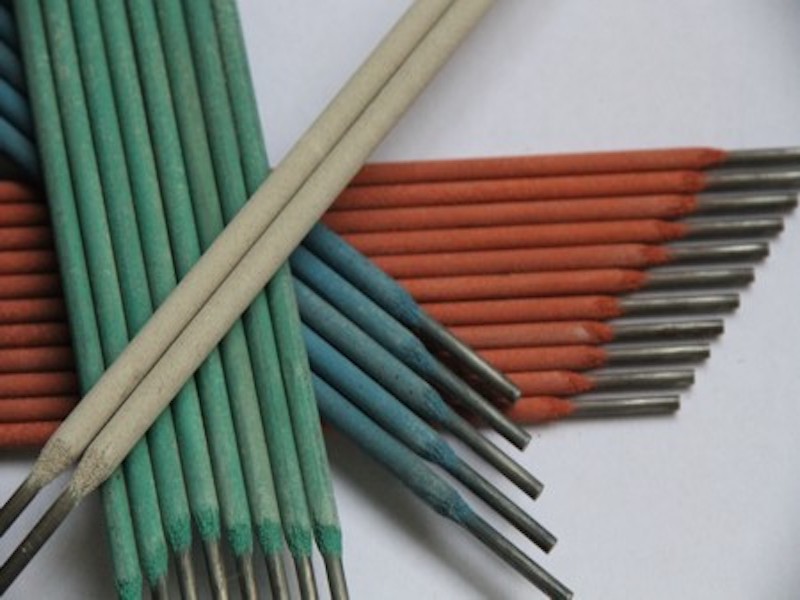

2. Welding Position: Determine the welding position(s) you will be working in, as specific electrodes are designed to perform optimally in certain positions. Choosing the appropriate electrode for the welding position enhances the quality and integrity of your welds.
3. Welding Technique: Consider the welding technique you will be using. For example, if you prefer to use a stick, TIG, or MIG welding method. Different techniques may require specific types of electrodes for optimal welding results.
Price of Classification of Welding Electrodes:
The pricing of welding electrodes varies based on several factors, including the brand, coating composition, electrode quality, and package quantity. Higher-quality electrodes made by reputable manufacturers tend to command a higher price due to their superior performance and reliability. Additionally, electrodes with specialized coatings or those designed for specific applications might cost more than general-purpose electrodes.
Conclusion:
Understanding the classification of welding electrodes is crucial for selecting the right electrode for your welding projects. Coating composition, welding position suitability, and application-specific classifications are essential factors to consider when making a purchase decision. By carefully assessing your welding requirements and conducting thorough research, you can ensure you invest in the right welding electrodes that deliver impeccable weld quality and durability.
(Word Count: 690)